Declaring constants in VB.Net
In this article we will see a small example of using constants in vb.net . constants are declared with a keyword const .
Example :
ConstPI As Double = 3.14
ConstmyStr As String= “*** www.ProgrammingPosts.blogspot.com ***”
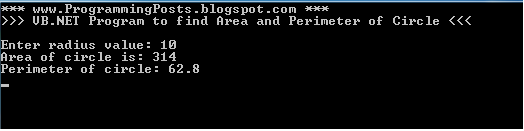
The program below is to find the area and perimeter of circle in which we use const .
In the program below we have declared PI as a constant of type double which value is given as 3.14 and
myStr is a const of type string .
It means PI value cannot be changed either at compile time or run-time .
If we try to assign the value to constant it gives a compile time error .
Any Integral or string variables can be declared as constants.
We can also declare constants as public to use it in all the classes in a program.
Module Module1
Sub Main()
‘declaring const variable PI
ConstPI As Double = 3.14
ConstmyStr As String= “*** www.ProgrammingPosts.blogspot.com ***”
Console.WriteLine(myStr) ‘here myStr is a string constant
Console.WriteLine(“>>> VB.NET Program to find Area and Perimeter of Circle <<<“ & vbLf)
Console.Write(“Enter radius value: “)
Dim r As Integer = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine()) ‘taking radius as input
Dimarea As Double= PI * r * r ‘getting area of circle
Console.WriteLine(“Area of circle is: “ & area)
‘if we try to assign a value to PI or myStr , we get compile-time error
‘PI = 123
‘myStr = “this is new string”;
Dimperimeter As Double= 2 * PI * r ‘getting perimeter of circle
Console.WriteLine(“Perimeter of circle: “ & perimeter)
Console.Read()
End Sub
End Module
Sample Output :